
S-26 Goat Milk - Is It a Good Option for Your Child?
GOATS WERE ONE OF THE FIRST DOMESTICATED FARM ANIMALS

DOMESTICATED 10,000 YEARS AGO 2 Goats are stronger farm animals that can adapt to desert, mountainous, and tropical areas where other livestock species would not thrive.2
GOAT MILK HAS A LONG HISTORY OF USE AND CONTINUES TO BE POPULAR TODAY
Preferred choice in the Middle East3

Approved by EFSA, 2012 as a suitable protein source for infant and follow-on formulae4
EFSA:European Food Safety Authority
IS GOAT MILK GOOD FOR YOUR BABY? Goat milk has several unique characteristics that can make it a gentle and nutritious alternative source of milk.5-8
 Easy-to-digest5-6
Easy-to-digest5-6 Brain development5
Brain development5 Stronger immunity5
Stronger immunity5 Less allergenic*6-7
Less allergenic*6-7 High level of important nutrients6, 8
High level of important nutrients6, 8
A recent survey conducted shows around 42% mothers are likely to switch to Goat milk9
NATURE ENHANCED BY SCIENCE

High quality easy-to-digest protein with essential vitamins, minerals and nutrients to support healthy growth 7,20,27

A naturally occurring probiotic in breast milk with proven benefits10-13 Boosts Immunity10-13 Gut Friendly10-13

An essential nutrient that helps support brain and eye development14,15

90% of our goat milk originates from Austria and Netherlands 16

Use of high-quality goats of selective breeds: Saanen goats-white*16 *Saanen goat milk has higher oligosaccharide content

World renowned for producing premium products

S-26® GOAT MILK 3 IS THE FIRST AND ONLY GOAT MILK WITH PROBIOTIC L. REUTERI

BOOSTS IMMUNITY
Promotes immunity by regulating immune cells10-13


SUPPORTS GUT COMFORT
Promotes healthy gut flora, maintains intestinal barrier and helps reduce gastrointestinal symptoms10-13
L. REUTERI IN S-26® GOAT MILK 3 MAY HELP TO STRENGTHEN IMMUNITY AND GUT HEALTH
S-26® GOAT MILK 3 CONTAINS A NATURALLY EASY-TO-DIGEST GOAT MILK PROTEIN, THAT IS CLOSER TO HUMAN MILK IN DIGESTIBILITY21
Digestion Efficiency

HIGH LEVELS OF DHA IN S26® GOAT MILK 3 SUPPORTS BRAIN AND VISUAL DEVELOPMENT

Improves mental development14

Supports future learning14,23

Supports visual development & acuity15,22

Supports achievement of language & motor milestones23
GOAT MILK CONTAINS ADDITIONAL INGREDIENTS THAT OFFER BENEFITS TO THE BABY
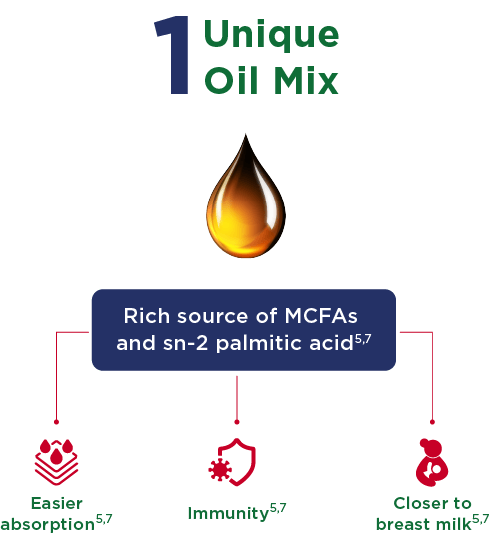
Oil Mix
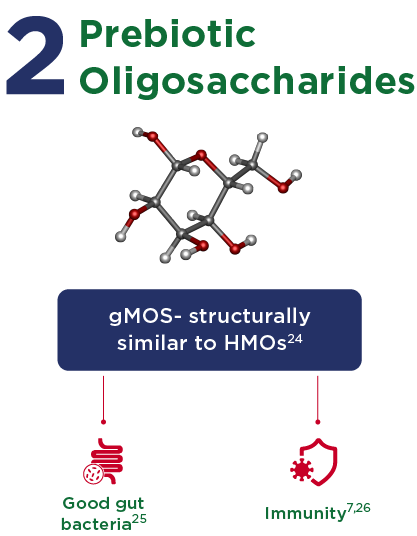
Oligosaccharides
Preparation methods
Wash your hands before preparing baby’s formula.
Wash cup thoroughly until no milk remains.
Boil for 5 minutes, leave covered until use.
Boil drinking water for 5 minutes; allow to cool until luke warm.

Consult feeding table, pour exact amount of lukewarm water into the cup.
Use only the scoop from this container. Powder must be leveled.
Consult feeding table, add exact number of level scoops into cup.
Stir until powder completely dissolves. To be consumed within 1 hour.
Close tin tightly after each use & store it in a cool & dry place. Must be used within 3 weeks after opening.
Warning: Unboiled water, unboiled cups or incorrect dilution can make your child ill. Incorrect storage, handling, preparation and feeding can potentially lead to adverse effects for the health of your child.





IMPORTANT NOTICE: We believe that breastfeeding is the ideal nutritional start for babies and we fully support the World Health Organizations recommendation of exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life followed by the introduction of adequate nutritious complementary foods along with continued breastfeeding up to two years of age. S-26 GOAT MILK STAGE 3 is not a breast-milk substitute. We recommend that you speak to your healthcare professional about how to feed your baby and seek advice on when to introduce this product.


